This post discusses extensively what character formatting entails. You will learn how to perform character formatting tasks such as changing the font, font style, size, color, and other effects and animations, using the Format menu, formatting toolbar or shortcut keys. Characters are letters, numerals, spaces, punctuation marks and symbols entered from the keyboard/onscreen keyboard (such as @, #, %, & and *) or symbols inserted into the document from the Symbol dialog box or the Character Map (such as ®, ™, φ. ♥, ♫, », Ø, Σ, ∫, ∏, Φ, ☺, ≤, ∞, Ω, №, ß, etc). Character formatting in Word has to do with applying formatting properties to enhance the appearance of individual text characters. Character formats can be applied to a single character, word, sentence or a line of text, without such formatting affecting the entire current paragraph. Examples of character formats that can be applied to text characters in Word include those you find in the Font dialog box (such as bold, italic, underline, font, size, color, superscript, subscript, scaling, animation effects, etc), highlight, change case, etc. To apply a character format to a character or a set of characters, you need to specifically select the desired amount of characters and then apply the formatting you want. The following sections provide you extensive instructions on how to format text characters in Word. Change Font Font is referred to as the typeface for typed text. In a lame man's language, it can be called 'handwriting'. In real life, people scribble in unique handwritings characterized with different looks, sizes, intensity and spaces. Font is the electronic version of such handwritings. |
To change the font in which text is displayed in a Word 2002 document, use any of the following:
- Format Menu
- Formatting Toolbar
- Keyboard Shortcut
Change Font Using the Format Menu
- Select the text.
- On the Menu bar, click Format to display the Format menu.
- From the Format menu, click Font. The Font dialog box appears.
- If the Font tab page is not already displayed, click the Font tab to activate it.
- Select a font name in the Font box. The Preview box shows how text will be displayed in the selected font.
- Click OK button.
Change Font Using the Formatting Toolbar
- Select the text.
- On the Formatting toolbar, click the drop-down arrow in front of the Font box and click a font name from the font list.
Change Font Using Keyboard Shortcut
- Select the text.
- Press Ctrl + Shift + F. Word selects the current font name in the Font box on the Formatting toolbar.
- Type, or use the arrow keys to select a font name.
- Press ENTER.
Change Font Size
You can change the font size of text via- The Font dialog box
- The Formatting toolbar
- Shortcut keys
Change Font Size Using the Font Dialog Box
- Select the text.
- From the Format menu, click Font. Font dialog box appears.
- Type or select a font size in the Size box.
- Click OK.
Change Font Size Using the Formatting Toolbar
- Select the desired text.
- On the Formatting toolbar, type a desired number in Font Size box, or click the drop-down arrow in the Font Size box and select a desired font size from the Font Size drop-down list.
Change Font Size Using Shortcut Keys
- To decrease font size by one point (e.g. 12 to 11), press Ctrl + [ .
- To increase font size by one point (e.g. from 12 to 13), press Ctrl + ] .
- To decrease font size to the next smaller size (e.g. from 12 to 10), press Ctrl + Shift + <.
- To increase font size to the next larger size (e.g. from 12 to 14), press Ctrl + Shift + >.
- Select the desired text.
- Press Ctrl + Shift + P. The current font size becomes selected in the Font Size box on the Formatting toolbar.
- Type, or use the arrow keys to select a font size in the Font Size box.
- Press ENTER.
Changing Font Style
The font style in which text is displayed in Word 2002 can be changed using
- The Font command.
- The Formatting toolbar.
- Shortcut keys.
Change Font Style Using the Font Command
- Select the text.
- From the Format menu, click Font.
- In the Style box, select a font style (e.g. Bold, Italic, or Bold Italic)
- Click the OK button.
Change Font Style Using the Formatting Toolbar
Select the text whose font style you want to change, and do one or more of the following:
- On the Formatting toolbar, click Bold (button) to apply bold formatting to the selected text.
- On the Formatting toolbar, click Italic (button) to italicize the selected text.
Change Font Style Using Shortcut Keys
Select the required text, and do one or combination of the following:- Press Ctrl + B, to apply bold formatting.
- Press Ctrl + I, to italicize text.
Underline Text
One way to emphasize a portion of text in a document is to underline it. You can underline text using any of Font dialog box, Formatting toolbar, or keyboard shortcut. To underline text with a line style and/or color other than the default setting in your document, use the Font dialog box. In the dialog box, you can specify the underline style as well as the underline color.To underline text quickly using the default underline style, use the Formatting toolbar, or keyboard shortcuts.
Underline Text Using the Font Command
- Select the text to be underlined.
- On the Format menu, click Font. Font dialog box is displayed.
- Click Underline style box, and then click a desired style e.g. Words only.
- To make the underline appear in a color different from letter color, select a desired color from the Underline color box.
- Click the OK button.
NOTE:
If/since your computer is connected to the internet, the decorative line styles may appear dimmed in the list, and when selected, Word may display a message box stating that the line style you have selected has been disabled because it is not supported by target browsers such as Internet Explorer 4.0 or later or Netscape Navigator 4.0 or later.
When this happens, you can do one of two things:
A). If you intend to display the content of the document in a browser on the intranet/internet, simply stick to the default underline style which is supported and available on all browsers.
B). If you do not intend to display the document on a browser but simply want to use the desired underline style for decorative purpose, you can suppress the message box and make the underline styles available for use by doing the following:
- On the Tools menu, click Options and then click the General tab in the Options dialog box that appears.
- Click Web Options button, and then click Browsers tab in the Web Options dialog box that is displayed.
- Uncheck the Disable features not supported by these browsers check box.
- In the People who view this Web page will be using box, select choose your browser.
- Click OK to close the Web Options dialog box.
- Click OK to accept your settings and close the Options dialog box.
Underline Text Quickly Using the Formatting Toolbar
- Select the text to be underlined.
- On the Formatting toolbar, the Underline button.
- To remove the Underline formatting from text, select the text and Click the Underline button on the Formatting toolbar again, or use alternative methods.
Underline Text Quickly Using Shortcut Keys
- Select the desired text.
- Do one of the following:
- Press Ctrl + U to underline both text and spaces.
- Press Ctrl + Shift + W to underline words only.
- Press Ctrl + Shift + D to apply double underline style.
Apply Other Effects
Using the Font dialog box, you can apply or remove character formats, such as Hidden Text, Superscript, Subscript, shadows, etc. These formatting options appear under the Effects section of the Font tab page in the Font dialog box. They have check boxes beside them which can be checked (populated/marked, by clicking it using the mouse or by pressing the SPACEBAR on the keyboard when focus is on it) or unchecked (cleared/unmarked, by clicking it or pressing the SPACEBAR on the keyboard when it receives focus) to deselect or remove the effect from the selected text. You can select more than one of such effects and apply them to selected text at once by clicking the OK button. For example, you can check the boxes beside each of Superscript, Strikethrough and Small Caps to select them and then click the OK button to apply them at once to the selected text.
Note however, that some of these effects are mutually exclusive, in that selecting one of such mutually exclusive options makes selecting the other impossible, because both effects cannot be applied to the selected text at the same time. As a result, once you check the box next to one of such mutually exclusive options, Word automatically clears the checkmark from the other option.
Examples of pairs of mutually exclusive formatting effects in Word are:
- Strikethrough and Double Strikethrough.
- Superscript and Subscript.
- Emboss and Engrave.
- Shadow and Emboss.
- Shadow and Engrave.
- Outline and Emboss.
- Outline and Engrave.
- All Caps and Small Caps.
To apply one or more formatting effects to selected text,
- Select the required text.
- On the Format menu, click Font and then click the Font tab in the Font dialog box that appears.
- In the Effects section of the Font tab page, click the boxes next to the options you want.
- Click the OK button.
Tips:
You can also apply or remove effects using shortcut keys. Examples:
Press These Keys To Do This CTRL + SHIFT + A Apply All Caps formatting to letters. CTRL + SHIFT + K Apply SMALL CAPS formatting to letters. CTRL + SHIFT + W Underline words but not spaces. CTRL + SHIFT + D Format text with Double-underline. CTRL + SHIFT + H Apply Hidden Text formatting. CTRL + EQUAL SIGN Apply Subscript formatting. CTRL + SHIFT + PLUS SIGN Apply Superscript formatting. CTRL + SPACEBAR Remove manual character formatting.
Change Default Character Formatting
Normally, when you type in Word, text appears in a particular font (Times New Roman); style (Regular); size (12); color (Automatic, i.e. Black); and anytime you underline text, a single tiny line with color same as letter color is placed under the selected text. The aforementioned are some of the default character formatting for the Normal Style (the default text style) in Word and it is used in all new documents you create from the current document template.Sometimes, however, you choose a different font, style, size, etc, for text, if the preset style is not adequately desirable for your creativity. It you always create documents that use a (character) formatting different in some respects from the Default style, it will be preferable you change the Default (for the Normal Style) to make the new setting available for all new documents you create from the current document template. This will save you some hair, (believe me) in terms of time and effort!
To change the default character formatting
- On the Format menu, click Font. Font dialog box appears.
- Do one of the following:
- To set a new default font, type or select a font name in the Font box.
- To set a new default font style, select an option from the Font Style list box.
- To set a new default size, type or select the new size from the Size box.
- To set a new default text color, underline style, and other effects, select them in the appropriate boxes available.
- If necessary, click the Character Spacing tab or the Text Effects tab and make appropriate selections.
- Click the Default button. 'Surprised or wondering whether you simply clicked the button unknowingly' Word (or the Office Assistant) will display a dialog box asking you to confirm that you really want to change the default font to... for the NORMAL (current) template.
- Click YES.
- Save the the document.
Character Spacing
Characters are letters, numerals, symbols (such as #, $, ^, &, @, etc ), punctuation marks, and spaces. To enter text in Word, you hit the lettered keys on the keyboard and these input the labeled letters in the document. The letters so entered are closely placed horizontally next to each other to form words, with little spaces after each character (letter) forming the words. This is the normal (default) character spacing.Characters are combined to form words, with little spaces between them. Each character you enter has a little space after it. These after-a-character spaces are the spaces seen in-between the characters that form the words in a document. If you like, however, you can adjust the spacing between the characters forming words. This is called character spacing.
Character spacing can either increase or reduce the amount of space after a selected character by the amount you specify. Note that the adjustment depends on the font design and the specific letter pairs.
In Word, character spacing can take any of the following forms:
- Condensed e.g character spacing.
- Normal e.g character spacing.
- Expanded e.g character spacing.
- You can also specify automatic kerning to have Word reduce the spacing between certain letter pairs to improve the overall appearance of the selected text. Note that automatic kerning can be used only with proportionally spaced TrueType fonts (i.e. fonts having varying width for each character e.g. 'i'
and 'w' differ in widths) or Adobe Type Manager fonts. In other words, kerning occurs immediately for scaleable fonts larger than the minimum size you specify.
To adjust character spacing
- On the Format menu, click Font. Font dialog box is displayed.
- Click the Character Spacing tab.
- In the Character spacing tab page, do one or more of the following:
| TO | DO THIS |
Reduce the amount of space after the selected character or characters of the selected text | Select Condensed from the Spacing box or specify an amount in the By spin box. |
Reduce the amount of space after the selected character or characters of the selected text | Select Expanded from the Spacing box or specify an amount in the By spin box. |
Revert the amount of space after the selected character or characters of the selected text to the default | Select Normal from the Spacing box. |
Scale the selected text by an amount | Type or choose a scale percentage from the Scale box. |
Adjust the vertical positioning of the selected character(s) | Type or choose a percentage from the Position box. |
Specify the size at which kerning is performed on TrueType or Adobe Type Manager fonts | Check the Kerning for fonts box and enter a number in the spin box before Points and above. |
- Click the OK button.
Text Animation
Word also includes a bunch of effects you can use to dazzle up or animate a document onscreen. You should note the following about text effects:
- Animation options in Word are mutually exclusive, in that you can apply only one animation effect at a time.
- Animation effects are for on-screen display only: they cannot be printed with document.
- Animation effects can be applied to both text and graphics.
To apply animation effects to selected document content
- Select the document content (text and/objects) to be animated.
- On the Format menu, click Font and then click the Text Effects tab on the Font dialog box.
- In the Animations box, select the animation effect you want.
- Click the OK button.
Highlighting Documents
Sometimes when you read, you use a marker or other appropriate tools to mark points you want to find easily next time. This kind of operation is called highlighting in Word. In Word, you use the Highlight tool on the Formatting toolbar to mark and find important text or ponts in your document. The following sections provide you the steps needed to apply or remove highlighting from part or all of a document.| Apply Highlighting | |
| |
| |
Remove Highlighting from Part or All of A Document
- Select the text you want to remove highlighting from, or press CTRL+A to select all of the text in the document.
- On the Formatting toolbar, click the arrow next to Highlight, and then click None.
Copying Character Formatting
You can quickly and easily format text by copying character formats from selected text to other text you want in a document. Suppose you have formatted a line as 10-point Arial, bold italic, Pink colored and justified, you can easily copy these settings to other text or all text in the entire document by using either the Format Painter tool or shortcut keys.
Copy Character Formats Using the Format Painter
- Select the text whose format you want to copy.
- Do one of the following:
- To copy the formats to only one location, on the Standard toolbar, click the Format Painter button once.
- To copy the formats to several locations, on the Standard toolbar, double-click the Format Painter button.

- When the mouse pointer changes to a paintbrush with an I-beam pointer, select the text to be formatted.
- If you double-clicked the Format Painter button, select the text you want to format, release the mouse button, and then select additional text anywhere in the document.
- When formatting is over, click the Format Painter button again, or simply press the ESC key.
Copy Character Formats Using the Keyboard
- Select the text whose format you want to copy.
- Press Ctrl + Shift + C.
- Select the text to be formatted.
- Press Ctrl + Shift + V.
Removing Character Formatting
Sometimes it may be necessary to strip certain text of the character formats that you specifically applied to it using the Font dialog box, Formatting toolbar, or key combinations. The operation will then leave the text in its raw or default character formatting settings. Note though, that you cannot remove from text character formats that are part of the paragraph style of the text.
To remove character formatting from text
- Select the text that has the character formats that youi want to remove.
- Press Ctrl + Spacebar keys.
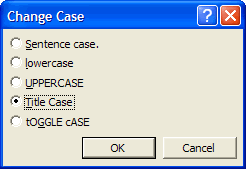
Change Case
You can change the capitalization of text quickly in Word using either the keyboard or the Change Case command on the Format menu. This saves you the stress of deleting and re-tying text in a different capitalization.Change Case Using the Keyboard
- Select the text whose case (capitalization) you want to change.
- Press Shift + F3 keys repeatedly until the text shows in the case (capitalization) you want.
Change Chase Using the Change Case Command
- Select the text whose capitalization you want to change.
- On the Format menu, choose the Change Case command. Change Case dialog box appears.
- Click the capitalization option you want in the Change case dialog box, and then click OK.
- Sentence case: capitalizes only the first letter in the selected sentences.
- lowercase: converts all selected text to lowercase letters ("small letters").
- UPPERCASE: converts all selected text to uppercase letters ("capital letters").
- Title Case: capitalizes the first letter of each word of the selected text.
- tOGGLE cASE: changes uppercase letters to lowercase letters and lowercase letters to uppercase letters for all the selected text.





(flattened).png)

